In a plumbing system, flanges are mechanical parts that join pipes, valves, pumps, and other pieces of machinery. They offer a way to link many pipe sections together as well as attach other parts to those pipes, forming a safe and leak-tight connection. In industrial environments including power generation facilities, chemical plants, oil refineries, and other systems that require the movement of fluids or gases, flanges are frequently employed.
Flanges serve a crucial role in industrial and commercial applications where pipes need to be connected, disconnected, or secured in a piping system. Their primary purpose is to create a strong and leak-tight connection between different components, such as pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment. Here are some common uses and applications of flanges:
Flange Standard: There may be unique flange standards for various industries and geographical areas (e.g., ANSI, DIN, JIS). Compatibility and security are ensured by adhering to the applicable standard.
Flanges play an important role to the smooth movement of liquids, gases, and vapors in the complex web of industrial infrastructure. These little but essential elements, which are sometimes rejected, link together different pipe system components to enable the efficient and secure transportation of fluids. In this essay, we will go deep into the realm of flanges to examine their significance, varieties, materials, and important factors influencing their choice and application.
The Importance of Flanges
Thinking of a big industrial complex, such as an oil refinery, a chemical facility, or a power plant. These huge buildings include a complex system of pipes that transfer gases and liquids. Pipe sections, valves, pumps, and other equipment may be easily assembled and disassembled thanks to flanges, which act as connectors. These connections are essential for the system’s upkeep, repairs, and general operation.
Types of Flanges
Flanges come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each designed for specific applications and conditions. Here are some common types:
- Weld Neck Flanges: These flanges are designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. They have a long neck that provides reinforcement and reduces stress at the joint.
- Slip-On Flanges: Known for their ease of installation, slip-on flanges slide over the pipe and are then welded in place. They are suitable for low-pressure systems.
- Blind Flanges: As the name suggests, these flanges seal off the end of a pipe or vessel. They are commonly used to close openings and prevent leakage in piping systems.
- Socket Weld Flanges: These flanges are similar to slip-on flanges but have a socket for pipe insertion, providing a smooth flow path.
- Lap Joint Flanges: Lap joint flanges are used when frequent dismantling is required. They consist of two parts – a backing flange and a stub end, allowing for easy disconnection.
- Threaded Flanges: Threaded flanges have internal threads and are used with pipes that have external threads. They are suitable for low-pressure applications.
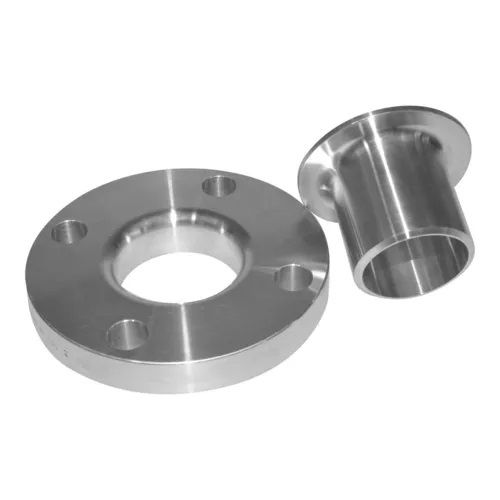
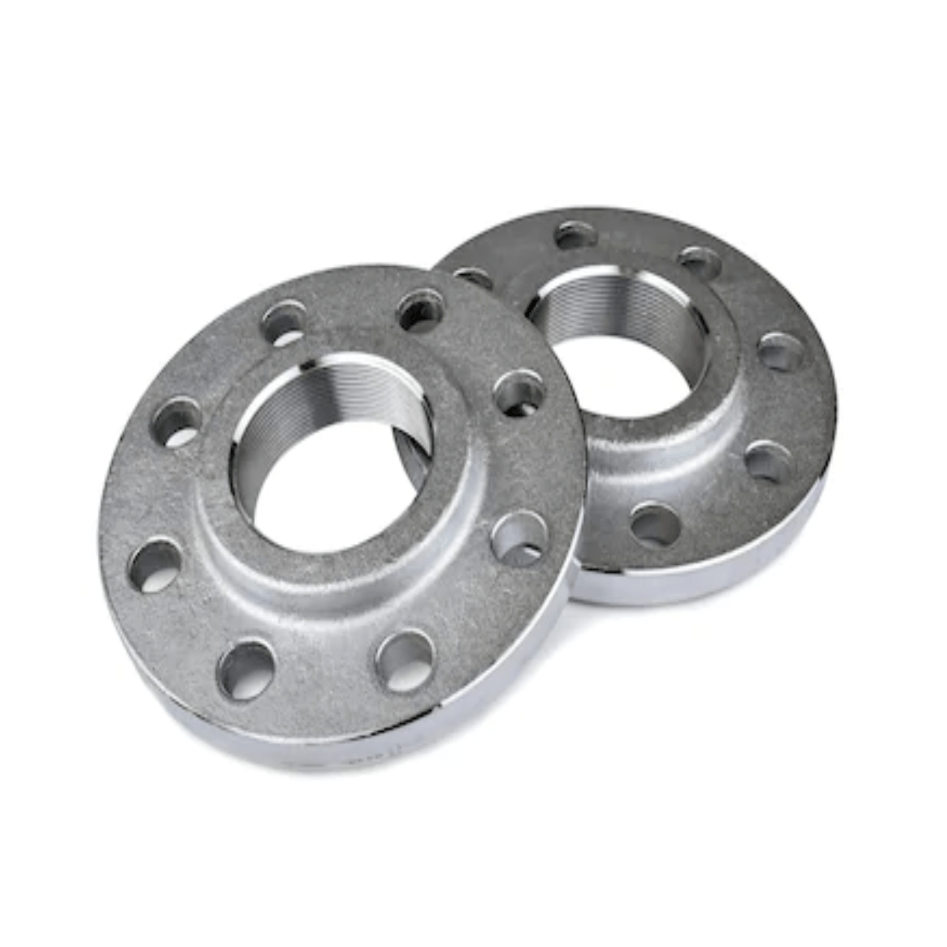



Materials for Flanges
The choice of material for a flange depends on factors such as fluid compatibility, temperature, pressure, and corrosion resistance. Common materials include:
- Carbon Steel: Suitable for general applications, carbon steel flanges offer good strength and affordability.
- Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance, stainless steel flanges are ideal for environments with high moisture or chemical exposure.
- Alloy Steel: Alloy steel flanges are designed to handle higher temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Duplex and Super Duplex: These materials combine the benefits of stainless steel and alloy steel, offering excellent corrosion resistance and strength.
- Non-Metallic Materials: Flanges made from materials like PVC, CPVC, or fiberglass-reinforced plastic are used in corrosive or non-metallic systems.
Considerations for Flange Selection
Make sure the chosen flange can handle the pressure and temperature requirements of the system.
Material Compatibility: To avoid rusting and contamination, use a material that is compatible with the fluid that is being moved.
The material used for the gasket should match that of the flange and be appropriate for the fluid and temperature conditions.
Flange Standard: There may be unique flange standards for various industries and geographical areas (e.g., ANSI, DIN, JIS). Compatibility and security are ensured by adhering to the applicable standard.
Conclusion
Flanges are the foundation of every pipe system, assuring its reliability, effectiveness, and safety even though they are sometimes out of view. Flanges are deserving of attention for their crucial function in industrial processes, from their many types and materials to the important factors in their selection. Consider the hidden heroes—the flanges—who keep a system of pipes, valves, and fittings together and operating efficiently the next time you see one.
Visit More