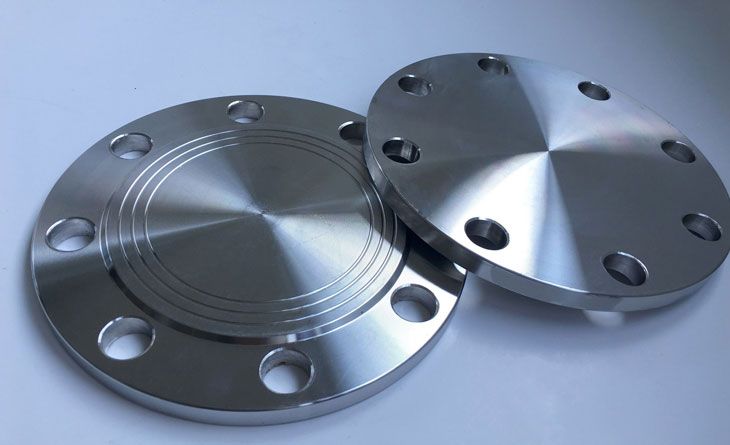
Blind flanges are an essential part of plumbing and piping systems. They are utilized to stop the flow of fluids, gases, or other substances by capping a pipe’s end or a vessel’s opening. Blind flanges are available in a variety of sizes, materials, and types, each with unique uses in distinct industrial applications.
We shall delve further into the world of blind flanges in this extensive guide. We hope to offer insightful information that will aid readers in developing a complete understanding of these crucial components, from comprehending their fundamental function to investigating various types and materials.
What are Blind Flanges?
The ends of pipes, valves, and pressure vessels are sealed with solid discs called blind flanges, often referred to as blank flanges. These flanges are perfect for stopping the flow of media in a piping system because they don’t have a center bore. Blind flanges are frequently utilized during maintenance or when additional pipeline additions are envisaged.
The Importance of Blind Flanges in Piping Systems
Blind flanges are essential for maintaining the effectiveness and safety of piping systems. They are important for the following reasons, among others:
Blind flanges offer a tight seal that shields against leaks from the closed end of vessels and pipes.
Isolation: They make it possible to securely carry out maintenance and repairs by enabling the isolation of a pipeline portion.
Blind flanges aid in the internal pressure containment of the piping system.
Expansion and Future Extensions: Should the need arise, they provide a blank slate for future expansions.
Types of Blind Flanges
Blind flanges come in a variety of varieties, each suited for a particular application. Typical types include:
Raised Face (RF) Blind Flanges, number
1. A raised gasket face on the Raised Face Blind Flange enables better alignment and connection. Low-pressure applications frequently employ this kind of flange.
- Blind Flanges with a Flat Face (FF)
Due to its flat surface, the Flat Face blind flange is perfect for low-pressure systems using non-metallic or unconventional gaskets.
Materials Used for Blind Flanges
Blind flanges can be made from a variety of materials to accommodate a range of settings and applications. Typical materials consist of:
Ideal for general-purpose applications and systems with modest pressure is carbon steel.
Stainless steel is suitable for harsh settings since it is corrosion-resistant.
High-temperature and high-pressure applications use alloy steel.
Duplex Steel: This stainless steel combines the strengths and corrosion resistance of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels.
How to Install Blind Flanges
To provide a solid and leak-free connection, blind flange installation calls for careful consideration. Here is a detailed instruction:
Make sure the flange and pipe ends are clean and free of any debris or impurities when preparing the surface.
Apply Gasket: Align the bolt holes as you place the gasket on the flange face.
The blind flange should be carefully positioned in relation to the pipe end and gasket.
Insert Bolts: Place bolts into the holes provided, then uniformly tighten them with the recommended torque.
Conclusion
Blind flanges are crucial parts of the pipe and plumbing industries. The security and effectiveness of industrial activities are guaranteed by their capacity to seal off a pipe or vessel’s end. Blind flanges are suitable for a wide range of applications, from low-pressure systems to high-pressure and high-temperature situations, and come in a variety of types and materials.
When doing maintenance and repairs, time and money can be saved by being aware of the many types of blind flanges and knowing how to install them properly. No matter what industry you work in—oil and gas, petrochemicals, water treatment, or any other—blind flanges are essential to preserving the structural integrity of your piping networks.